Clinical Waste
Clinical Waste
Clinical waste is defined as any waste that consists wholly or partly of:
- Human or animal tissue
- Blood or bodily fluids
- Excretions
- Drugs or other pharmaceutical products
- Swabs or dressings
- Syringes, needles or other sharp instruments which, unless rendered safe, may prove hazardous to any person coming into contact with it.
Clinical waste also refers to any other waste arising from medical, nursing, dental, veterinary, pharmaceutical or similar practice, investigation, treatment, teaching or research.
If clinical waste is not properly dealt with it can become a dangerous pollutant that can cause significant damage to the environment. Dangerous to individuals and the surrounding environment

A Long Term Solution for Clinical Waste Management
Pyrolysis Gasification
- Pyrolysis is the breakdown of waste with high heat temperatures in the absence of oxygen.
- Without oxygen, toxic products of partial combustion such as dioxins and furans cannot be formed, therefore we have clean disposal of waste
- Heat derived from the disposal of waste can create enough power for the system to be self-sustaining.
Benefits of Pyrolysis
- Clean form of waste disposal
- Eliminates environmentally harmful methane production
- Controls emissions of dioxins and furans with levels dramatically lower than regulation
- Pyrolysis facility is self-sustaining and doesn’t require external fuel, except for start-up
- Reduction of residuals by up to 95%, which can be sent to the landfill (ash)
- Produces energy for alternative uses
- Transforms clinical waste into an energy resource
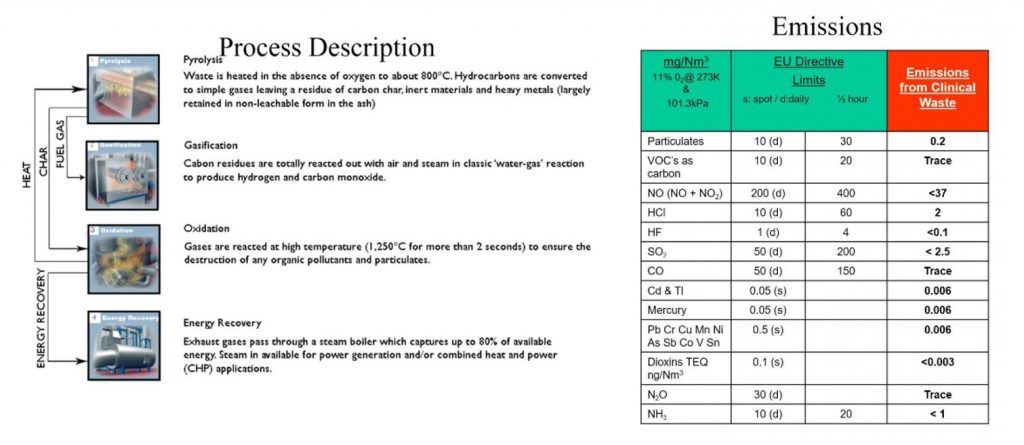
Compact Power, Avonmouth, UK
Clinical Waste Pyrolysis System

